 This is Online Notes on Chapter=1 ( Chemical Reactions and Equations)) Part 2 for preparation of CBSE BOARD Examination, NTSE etc.
This is Online Notes on Chapter=1 ( Chemical Reactions and Equations)) Part 2 for preparation of CBSE BOARD Examination, NTSE etc.=> TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS:
I. COMBINATION REACTION : The reaction in which two or more reactant combine to form a single product.
e.g. (i) Burning of coal
C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
(ii) Formation of water
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
(iii) CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq)
Quick lime Slaked lime
=> Exothermic Reactions : Reaction in which heat is released along with formation of products.
e.g., (i) Burning of natural gas
CH4 (g) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g) + Heat
(ii) Respiration is also an exothermic reaction.
C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2 (g) → 6CO2 (aq) + 6H2O (l) + energy
II. DECOMPOSITION REACTION : The reaction in which a compound splits into two or more simple substances is called decomposition reaction.
A → B + C
• Thermal decomposition : When decomposition is carried out by
heating.
e.g., (i) 2FeSO4 (s) ==HEAT==> Fe2O3 (s) + SO2 (g) + SO3 (g)
(Ferrous sulphate) (Ferric oxide)
Green colour Red-brown colour
(ii) CaCO3 (s) ==Heat==> CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
(Lime stone) (Quick lime)
• Electrolytic Decomposition : When decomposition is carried out by
passing electricity.
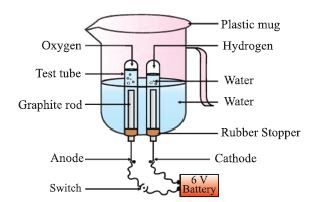
e.g., 2H2O ==Electric current==> 2H2 + O2
e.g., 2AgCl (s) ==Sunlight==> 2Ag (s) + Cl2 (g)
2AgBr (s) ==Sunlight==> 2Ag (s) + Br2 (g)
* Above reaction is used in black & white photography.
• Endothermic Reactions : The reactions which require energy in the
form of heat, light or electricity to break reactants are called endothermic
reactions.
III. DISPLACEMENT REACTION : The chemical reaction in which more reactive element displaces less reactive element from its salt solution.
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
The iron nail becomes brownish in colour by deposition of Cu and blue colour of
CuSO4 changes dirty green colour due to formation of FeSO4.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Zn is more reactive than copper.
IV. DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTION : A reaction in which new compounds are formed by mutual exchange of ions between two compounds.
Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (aq)
(Sodium (Barium (Barium (Sodium
sulphate) chloride) sulphate) chloride)
White precipitate of BaSO4 is formed, so it is also called precipitation reaction.
V. OXIDATION AND REDUCTION :
Oxidation :
i) The addition of oxygen to substance.
(ii) The removal of hydrogen from a substance.
C + O2 → CO2
2Cu + O2 ==Heat==> 2CuO
CuO + H2 ==Heat==> Cu + H2O
Reduction :
(i) The addition of hydrogen to substance.
(ii) The removal of oxygen from a substance.
In this reaction CuO is reduced to Cu and H2 is oxidized to H2O. So, oxidation and reduction taking place together is redox reaction.
=> Effects of Oxidation in Daily Life:
1) Corrosion :
• When a metal is exposed to substances such as moisture, acid etc. for some
time, a layer of hydrated oxide is formed which weakens the metal and hence
metal is said to be corrode
• Rusting of iron, black coating on silver and green coating on copper are
examples of corrosion.
• Corrosion can be prevented by galvanization, electroplating or painting.
2) Rancidity : The oxidation of fats and oils when exposed to air is known as
rancidity. It leads to bad smell and bad taste of food.
=> Methods to Prevent Rancidity :
(i) By adding antioxidants
(ii) Keeping food in air tight containers
(iii) Replacing air by nitrogen
(iv) Refrigeration.



No comments:
Write comments