 These are Online Formulas on "Chemical Kinetics" ( Chapter=> 4) for
These are Online Formulas on "Chemical Kinetics" ( Chapter=> 4) for practice of CBSE BOARD, CBSE NEET, CSIR NET Chemical Science etc.
Formulas List on "Chemical Kinetics":
1. Instantaneous rate = dx / dt
where dx is small change in conc. and dt is the smallest interval of time.
2. Average rate = Δx / Δt
where Δx is change in concentration and Δt is large interval of time.
3. A + B → C + D
Rate of disappearance of A = - d[A] / dt
where d[A] is small change in conc. of ‘A’ and dt is small interval of time
Rate of disappearance of B = - d[B]/ dt
Rate of appearance of C = + d[C] / dt
Rate of appearance of D = + d[D] / dt
Rate = - d[A] / dt = - d[B] / dt = + d[C] / dt = + d[D] /dt
Unit of rate of reaction = mol L-1s-1
4. Order of reaction:
If rate law expression for a reaction is
Rate = k [A]x [B]y
Order of reaction = x + y
Remember: Order cannot be determined with a given balanced chemical equation. It can be experimentally determined.
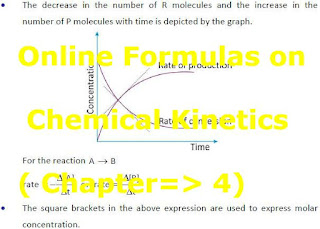
5. Integrated rate law for zero order reaction:
R → P
dx / dt = k[R]0
Unit of ‘k’ is mol L-1s-1
k = {[R0] - [R] }/ t
If we plot a graph between concentration of R vs time, the graph is a straight line with slope equal to -k and intercept is equal to [R0].
6. Half- life reaction for a for zero order reaction:
t1/2 = [R ] / 2k
7. Rate law for 1st order reaction:
R ==> P
k = (2.303 / t) (log [R0] / [R])
where ‘k’ is rate constant or specific reaction rate, [R0] is initial molar
conc., [R] is final molar conc. after time‘t’.
If we plot a graph between ln[R] with time, we get a straight line whose
slope = - k
and intercept ln[R0]
k = (2.303 / t) (log [a] / [a - x])
where ‘a’ is initial conc. in mol L-1, x mol L-1 have reacted in time ‘t’
final conc., after time ‘t’ is (a – x).
8. Half- Life for a first order reaction is:
t1/2 = 0.693 / k
9. Formula to calculate rate constant for first order gas phase reaction
of the type
A(g) ==> B(g) + C(g)
k = (2.303 / t) (log [Pi] / [Pi - Pt])
Where:
Pi is initial pressure of A
Pt is total pressure of gaseous mixture containing A , B, C
Remember:
pt = pA + pB + pC
10. Arrhenius equation:
k =Ae -Ea /RT
11. log ( k2 / k1) = ( Ea / 2.303 RT ) [ (T2 -T1 ) / T1T2 ]
12. Rate = P ZAB . e -Ea /RT
Where: ZAB represents the collision frequency of reactants, A and B
e -Ea /RT represents the fraction of molecules with energies equal to or greater than Ea
P is called the probability or steric factor.

No comments:
Write comments